How to Create a Chained Data Transformation
Complex ETL and data integration projects rarely fit into a single transformation. Developers often build multi-stage data pipelines where the output of one step becomes the input for the next. This approach makes it easier to manage dependencies, reuse logic, and keep large workflows maintainable. Breaking transformations into smaller, staged mappings also simplifies testing, debugging, and long-term scalability.
Altova MapForce supports this approach through chained data mapping, allowing you to connect multiple transformations into a structured processing workflow. This article explains when to use chained transformations, the problems they solve in real-world data pipelines, and how to build a modular, multi-stage workflow in MapForce.

Benefits of Chained Data Processing
There are multiple advantages to the chained data transformation approach, especially when handing complicated ETL and data integration workflows. (Want the quick version? Check out this how-to video to see how easy it is to build data pipelines with multiple transformations using visual tools in Altova MapForce.)
Benefits of creating a step-by-step data conversion process include:
Simplifying complex data processing: A chained data mapping approach makes it easier to handle complex data processing tasks by breaking the transformation down into smaller, manageable stages. Each link in the chain performs a specific operation on the data, making it easier to understand, test, and maintain.
Easy troubleshooting: By design, each transformation in the chain is responsible for a specific aspect of data manipulation. This makes the mapping easier to understand and makes it easier to identify and isolate errors or issues that may occur during the processing.
Flexibility and adaptability: Multi-stage data transformation offers flexibility for handling different data scenarios. Developers can easily modify or extend the chain by adding, removing, or rearranging transformations to accommodate new requirements or variations in input data. This adaptability is important if data processing needs evolve over time.
Easy understanding and maintenance: Sequential data transformation helps make a mapping project easier to understand and maintain. Each step in the chain represents a clear transformation operation, making it easier for team members to understand the overall data flow and logic. And if a bug or issue arises, developers can pinpoint the problematic step and debug it in isolation without affecting the rest of the workflow.
Defining Multi-Stage Data Transformations
MapForce offers a no-code, graphical approach to defining each step on the data conversion process. The visual representation provides a clear overview of the entire data pipeline and its individual stages, making it easy to understand and modify.
MapForce ships with a rich library of data processing filters and functions for defining data transformation rules and building more complex, visually defined functions. Instant output facilitates testing and troubleshooting.
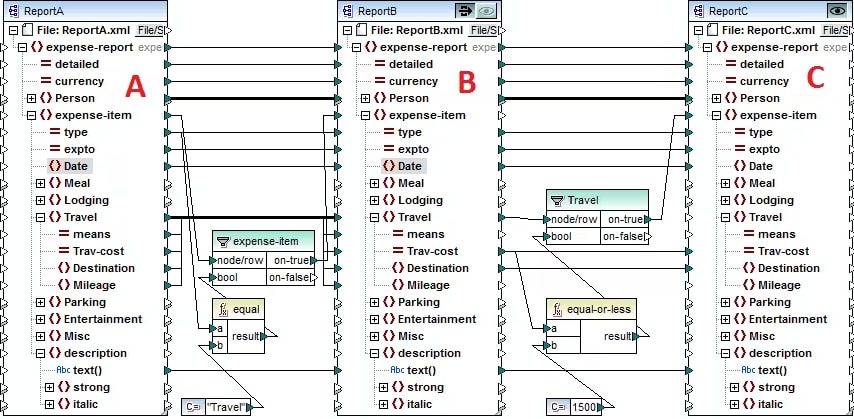
In a multi-step data mapping, at least one component acts both as a source and a target. This intermediate component (labeled B above) creates output that is then used as input for further processing in the next step in the chain. Chained steps in MapForce include the “pass-through” feature, which allows you to preview the output produced at each stage of the mapping for quick troubleshooting. For example, in the mapping above, you can preview (and save) the output resulting from transformation A to B, as well as the output resulting from B to C.
Though this example shows a chained XML mapping, MapForce is an any-to-any data mapping tool with support for converting between any combination XML, SQL and NoSQL databases, JSON, text, Excel, EDI, Shopify, and more.
Watch this video to see how chained data transformation works. The example shows a multi-step data mapping from XML to JSON to CSV and covers the use of data filtering and sorting functions. You will learn:
- How to reuse the output of one transformation in another
- How to split complex data transformations into smaller steps
- The advantages of breaking large ETL workflows into modular mappings
- How to managing dependencies in complex mappings
- How to build reusable transformation components
You can explore chained data mapping yourself by downloading a free, 30-day trial of MapForce and opening the Chained Mapping that is included in the MapForce examples project.