Build an MQTT-enabled App
As IoT adoption accelerates, developers are increasingly tasked with connecting large numbers of distributed devices across unreliable or bandwidth-constrained networks. In these environments, the choice of communication protocol is critical. MQTT has become a widely adopted standard for IoT and event-driven systems because of its lightweight footprint, low latency, and efficient publish/subscribe messaging model.
MQTT is flexible enough to support everything from small proof-of-concept automation projects to large, production-scale deployments. It enables real-time data exchange between devices while minimizing network overhead, making it well suited for scenarios such as sensor networks, industrial automation, and remote monitoring.
Altova MobileTogether includes native support for building MQTT-enabled apps for iOS, Android, and Windows. Its low-code, rapid mobile app development (RMAD) approach allows developers to integrate MQTT messaging into cross-platform applications quickly, while still retaining control over app logic and data handling.
Let’s see how it works.

MQTT Messaging Protocol
An OASIS standard messaging protocol, MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) enables device-to-device telemetry in scenarios where low bandwidth, high latency, or an unreliable network connection is a concern. This lightweight protocol has a publish/subscribe architecture designed for reliable communication among devices, making it ideal for IoT scenarios.
MQTT’s decentralized model of communication allows devices to publish information to a central broker and subscribe to topics of interest. The broker filters messages based on their topic. Clients subscribe to one or more topics and receive the corresponding messages from the broker. Clients can both publish and subscribe to topics.
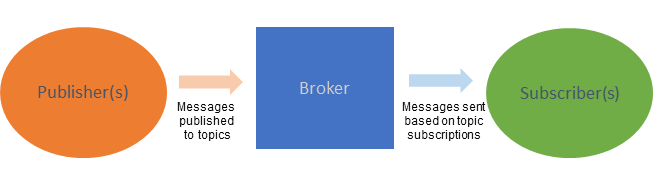
Its lightweight nature ensures minimal bandwidth usage and low latency, making MQTT a good choice for resource-constrained environments, such as those running IoT devices with limited processing power and bandwidth. At the same time, MQTT is highly scalable and can support connections among millions of smart devices.
MQTT is used in scenarios including smart home, smart office, and smart city systems. Today, the protocol is especially critical in industrial automation.
Automating Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT (IIoT) applications that use MQTT for device communication span industries including manufacturing, healthcare, energy, and oil and gas. In these systems, MQTT is often used to move telemetry and event data between sensors, edge devices, and backend services, providing reliable, low-overhead messaging in environments where network conditions and device capabilities can vary significantly.
For instance, in a smart factory utilizing MQTT, sensors on the production line publish real-time data on machine status and quality metrics to a central broker. Utilizing an app that subscribes to these topics allows plant managers to make instant decisions, optimize processes, and enhance overall efficiency.
Here are some common benefits of using MQTT in industrial automation:
| MQTT | Benefit for IIOT |
|---|---|
| Efficient & lightweight communication | Lightweight design minimizes protocol overhead, making it well suited for large numbers of distributed industrial devices. |
| Real-time monitoring, alerts, & control | Publish/subscribe model supports real-time transmission of sensor data and equipment status for responsive monitoring and control. |
| Scalability for large-scale deployments | Scales efficiently as device counts grow, maintaining reliable communication in large IIoT environments. |
| Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication | Enables asynchronous, autonomous data exchange between machines using a decoupled publish/subscribe model. |
| Remote monitoring & maintenance | Real-time status updates support remote diagnostics and maintenance, helping reduce downtime. |
| Energy efficiency | Low bandwidth usage and minimal overhead help reduce power consumption in constrained or battery-powered devices. |
| Interoperability & standardization | As a standards-based protocol, MQTT supports interoperability across devices from different manufacturers. |
Of course, these benefits apply equally to scenarios outside of industry, such as smart office and smart city systems.
What organizations need are easy-to-use client applications for managing and monitoring automation facilitated through MQTT. That’s where Altova MobileTogether comes in.
How to Build MQTT-enabled Apps
Altova MobileTogether is a low-code, highly affordable solution for building MQTT-enabled apps for monitoring and managing communications among smart devices. Whether you need to build a dashboard for remote monitoring or a client for real-time operations management, MobileTogether can get your MQTT solution out the door in record time.
With MobileTogether, you build once to generate apps for iOS, Android, and Windows devices as well as an HTML5 browser-based client (write once, deploy everywhere).
Take a look at a quick example of an app we created to demonstrate this functionality in a smart home automation scenario:
MQTT support in MobileTogether allows apps to join an MQTT network as a publisher, a subscriber, or both.
The development environment uses a combination of drag-and-drop UI design, the powerful Action Tree visual programming language for event handling, and standardized functional programming for data selection and processing. This unique, low-code approach makes it easy to define and test the various aspects of an MQTT-enabled app:
Set up a solution that can subscribe and unsubscribe to topics, publish messages, and disconnect from a broker
Integrate rich charts, graphs, and dashboards
Specify the actions to perform when the solution receives an MQTT message
Set up an MQTT service
Simulate and debug app behavior during development using recorded, real-world input
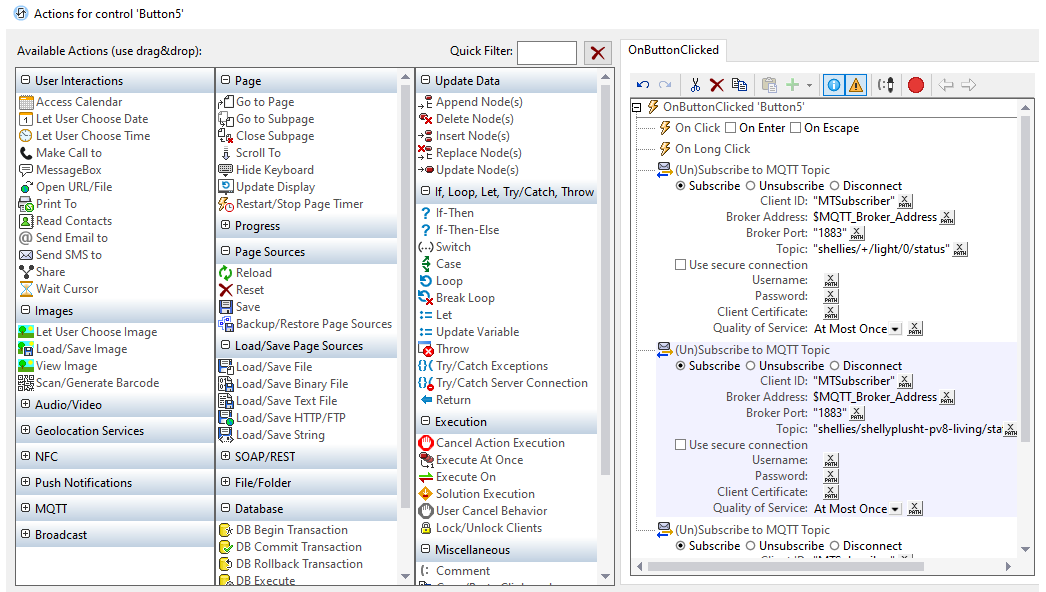
The comprehensive and easy-to-implement MQTT support in MobileTogether gives developers the flexibility to build a wide range of apps for industrial automation and other smart device systems.
It’s easy to get started building your first MQTT-enabled app in MobileTogether, which includes comprehensive documentation on MQTT app development in the Help file accessible when you download the free MobileTogether Designer.