Defining Local Relationships
When database tables do not have relationships between them, you can create primary and foreign key relationships between columns of different tables directly in MapForce (i.e., local relationships). Any database columns can be used as primary or foreign keys. You can also create new relations in addition to those existing in the database. Locally defined relationships are saved together with the mapping.
The following table lists all the possible fields between which you can define local relations. Mixed relationships are possible (for example, mapping the output of a stored procedure to a database column). The fields taking part in the relationship must have the same, or a compatible, data type.
Primary/unique key | Foreign key |
|---|---|
•Column of a database table or view •Output parameter or return value of a stored procedure, see also Stored Procedures •Column of a recordset returned by a stored procedure* •Column of a user-defined SELECT statement, see also SQL SELECT Statements as Virtual Tables. | •Column of a database table or view •Input parameter of a stored procedure •Input parameter of a user-defined SELECT statement |
* Applicable if the stored procedure is called either as data source (without parameters) or as a function (with input and output parameters). In order for the recordset to become available for selection, you must execute the stored procedure once, to retrieve the recordset.
Example
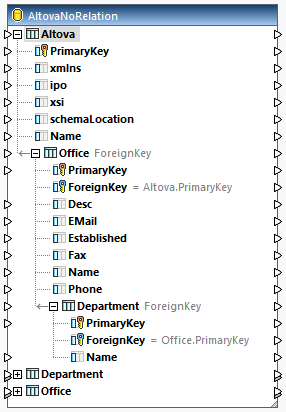
In the AltovaNoRelation.sqlite database (stored in the Tutorial folder), there is a primary key in each table, but foreign keys have not been defined yet (screenshot below).
In this example, our goal is to reference the Altova table in the Office table and the Office table in the Department table. Follow the instructions below:
1.Add the AltovaNoRelation.sqlite database to your mapping and select all the user tables.
2.Click the Add/Edit Relations button in the Insert Database Objects dialog.
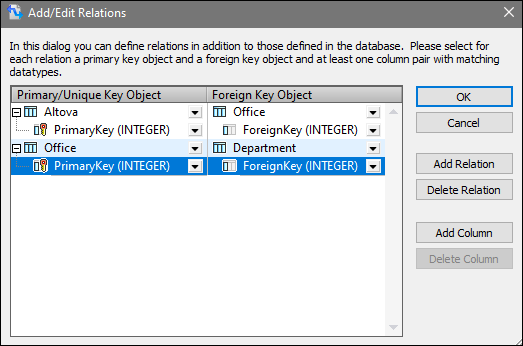
3.Click Add Relation in the Add/Edit Relations dialog (screenshot below).
4.Click [select object] in the Primary/Unique Key Object column and select Altova. Then select PrimaryKey in the [select column] drop-down list.
5.Click [select object] in the Foreign Key Object column and select Office. Then select ForeignKey in the [select column] drop-down list. Steps 4 and 5 create a primary-and-foreign-key relationship between the Altova and Office tables.
6.Add a new relation, click [select object] in the Primary/Unique Key Object column, and select Office. Then select PrimaryKey in the [select column] drop-down list.
7.Click [select object] in the Foreign Key Object column and select Department. Then select ForeignKey in the [select column] drop-down list.
8.Click OK to complete the local relation definition.
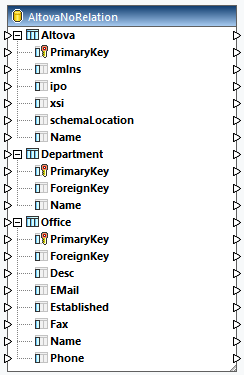
As soon as you have finished defining the local relations, the AltovaNoRelation component becomes available in the mapping area (screenshot below). The component displays three possible database structures. In each of these structures, the root table is different. For example, in the expanded structure below, Altova is the root table. Depending on your needs, you can map data from any of the structures available in the component. You can also mix and match tables from different structures. For more information about database relations, see Handling Database Relationships.