Logging
The Logging tab provides settings for the logging features of MobileTogether Server. If you modify any setting, click Save at the bottom of the tab for the modified setting to take effect.
Logging
Logs contain reports of workflow activity, and they are displayed in the Log tab of the Web UI. The settings in the Logging pane define logging parameters.
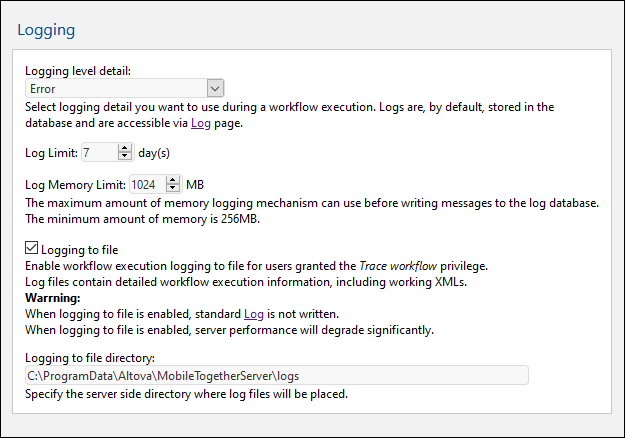
•Logging level detail: The detail can vary from: (i) logging only errors, (ii) through logging errors and warnings, and (iii) (most detailed) logging errors, warnings, and information.
•Log limit: Specifies for how long logs are kept.
•Log memory limit: Writing messages to the log DB is given a lower priority than the executing of workflows. Consequently, messages are not written directly to the log DB, but are held in memory till a gap in workflow execution frees up processor time to write messages to the log DB. If, however, (i) there is no time to write messages to the log DB, and (ii) the amount of memory used for logging reaches the Log Memory Limit, then all the log messages in memory are discarded. A single log message then replaces the discarded messages; it records that the Log Memory was cleared. The Log Memory Limit option allows you to create more memory space (by specifying when to discard messages from memory) and so take the load off the server. Otherwise, the combination of processing load and memory load could end the MobileTogether Server process. Factors that affect your selection of the limit value will be: (i) the amount of memory on the machine, and (ii) the logging level detail. The lowest Log Memory Limit value you are allowed to enter is 256 MB.
•Log files: Users that have been granted Trace workflow privileges can have logs saved to file if the Logging to file option is selected. The directory where logs are saved is specified in the Logging to file directory option. Note that that standard Log is not generated if logging to file has been enabled.
Syslog
Syslog is a standard protocol used to forward system log or event messages to a specific server, called a syslog server. Developers often use a syslog server to collect logs from various machines in a central location for further analysis. Syslog is the default logging mechanism in Linux. On Windows, a syslog server will need to be installed. (Note that Windows Event Log cannot be use for this puropse.)
The Syslog settings pane (screenshot below) enables you to define the settings for the syslog server.
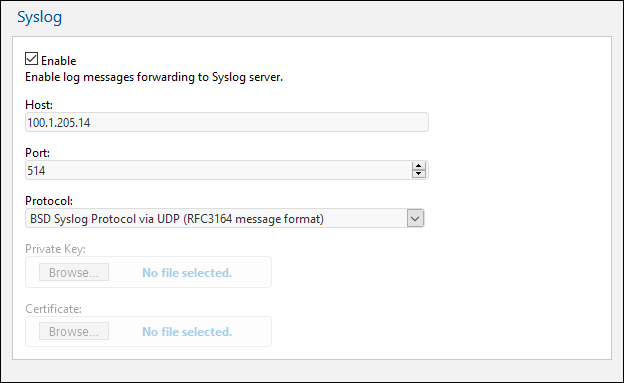
•The Host and Port settings are those of the Syslog server. Also see Notes below.
•Protocol: You can select from among the following protocols: BSD (UDP or TCP) or IETF (TCP or TLS/SSL). The BSD protocol provides the non-blocking UDP communication (which is, however, not a required communication property, because MobileTogether Server does not use any blocking). The IETF syslog protocol is recommended because it sends more information and supports secure communication. Additional information (about user, solution, and client-version) can be accessed in syslog server via macros: ${.SDATA.meta.user}, ${.SDATA.meta.session}, and ${.SDATA.meta.version}.
Notes
Linux usually comes with rsyslog pre-installed. Note, however, that syslog-ng is a more powerful option. The default ports (if not configured differently) are:
•BSD: 514 (for UDP and TCP)
•IETF: 601 via TCP
•IETF: 6514 via TLS
There are some additional syslog server settings that can be made via the config file. These settings are listed in the Config File Settings.