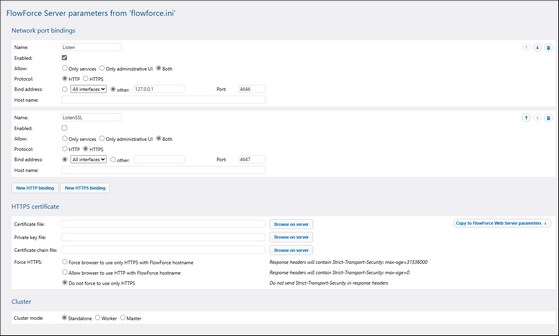
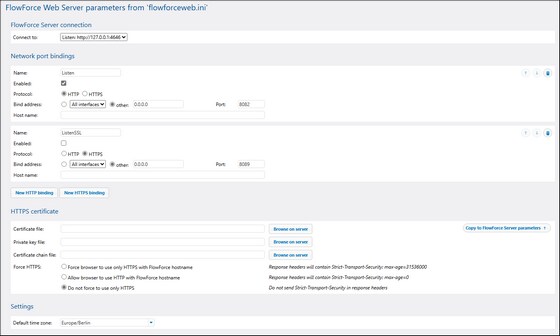
Configure Instance Parameters
The FlowForce Server Setup page enables you to configure various network settings, including the interfaces and ports on which FlowForce Server and FlowForce Web Server should listen. The parameters defined on the Instance Parameters page come from the following configuration files:
•flowforce.ini
•flowforceweb.ini
When you modify any parameters on the Instance Parameters page, the corresponding INI file is updated. To access the instance parameters, click Configure Parameters on the Setup page. The screenshots below illustrate the instance parameters for FlowForce Server and FlowForce Web Server, respectively.
The available parameters are described below.
Network port bindings
This section enables you to configure port bindings for FlowForce Server and FlowForce Web Server. Port binding refers to the process in which a network application is tied to a specific network port and IP address to listen for incoming connections. You can add, reorder, and remove bindings as needed.
The binding parameters you can configure are described in the table below.
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Name | Refers to the section name in the INI file. The name must start with Listen and can have any suffix after that. The name must be unique in the list.
|
Enabled | If this check box is selected, the binding is active. If the check box is cleared, the binding is deactivated, but its settings remain saved in the list.
|
This parameter enables you to restrict the binding to the Admin UI (FlowForce Web Server) only or to services only. You can also leave the binding unrestricted (Both).
If the interface binding is limited to services only or to the Admin UI only, other requests on that interface binding will result in HTTP error 404.
| |
Protocol | You can choose between HTTP (unencrypted) and HTTPS (encrypted). If you select HTTPS, you must provide the appropriate HTTPS certificates (see HTTPS Certificate below).
|
Bind address | The bind address specifies the network interface (IP address) the service should listen on. You can configure the service to listen on all interfaces, the localhost, or on a specific IP (the Other option).
If the binding address (interface) is non-local, you may need to configure the operating system's firewall so as to enable access through the designated port.
|
Port | The Port field specifies the network port number on which FlowForce Web Server/FlowForce Server should listen (e.g., 4647).
|
Host name | Specifies the name of the server machine as seen from other machines on the network. If left empty, the server automatically detects an appropriate host name.
This setting is relevant if the bind address is not local (127.0.0.1). The name can be a simple host name (e.g., somehost) or a fully qualified domain name (e.g., somehost.example.org) depending on your network configuration.
The host name is used for:
•Connecting from other machines or clients to the server •Executing services from the UI •SSL certificate validation (if HTTPS is enabled, the host name must match the certificate’s Common Name) •Communication between FlowForce Web Server and FlowForce Server over HTTPS •Altova ServiceController* on Windows •Generating clickable links in the web interface for jobs exposed as Web services
* Altova ServiceController is an application that enables you to conveniently start, stop, and configure Altova services on Windows systems.
|
Different binding configurations
Some of the possible binding configurations are described below.
FlowForce Server
Admin UI requirement:
•At least one port must allow the Admin UI (restricted to the Admin UI only or not restricted) so the FlowForce Web UI functions correctly.
•Only one port is needed for the Web UI to work; additional admin UI ports are not required.
•If only one port is used, configure the binding to be used for both the Web UI and services.
•You can choose between HTTP and HTTPS.
Optional service-only ports:
•You can add extra ports restricted to services only, which means users can call only jobs that are exposed as web services via their service URLs. An example is shown in the screenshot below:
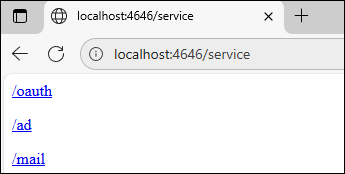
•You can choose whether a service-only port uses HTTP or HTTPS.
•You can define two port bindings if necessary: one for HTTP and one for HTTPS.
A service-only port has the following advantages:
•Improved security: Reduces the risk of exposing the Web UI and administrative functions to the network.
•Controlled external access: You can safely expose a port to external clients or networks for service calls without allowing configuration changes.
FlowForce Web Server
Web UI requirement:
•At least one port binding is required to serve the Web UI.
•You can choose HTTP or HTTPS.
Optional additional ports:
•You can define two port bindings if necessary: one for HTTP and one for HTTPS.
HTTPS certificate
If you select HTTPS in the Network Port Binding section, you must provide the following files:
•Certificate file: The server certificate in PEM format.
•Private key file: The private key corresponding to the certificate, in PEM format. The key must not be encrypted.
You may also need to provide the certificate chain file (optional): A file containing all intermediate certificates in PEM format, joined together in a single file.
You can set the Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) response header for HTTPS requests, which reduces the chance of sensitive information being intercepted or manipulated. The following options are available:
•Force the browser to use only HTTPS with the FlowForce hostname: The header Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000 is added, which tells the browser to use HTTPS for this hostname only for the next 31,536,000 seconds (approximately 1 year). After receiving this header, the browser will reject HTTP connections to this hostname.
•Allow the browser to use HTTP with the FlowForce hostname: The header Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=0 is added, which tells the browser to stop enforcing HTTPS for this hostname. This removes any existing HTTP Strict Transport Security rules for the hostname, allowing HTTP connections again.
•Do not force the browser to use only HTTPS: No Strict-Transport-Security header is sent. The browser will retain its current HSTS state for this hostname. For example, if the browser previously received an HSTS header, it will continue enforcing HTTPS until the existing max-age expires.
Important HSTS settings are cached by the browser. Even after you have changed the setting Force the browser to use only HTTPS with the FlowForce hostname, the browser may continue enforcing HTTPS until the max-age period expires.
To immediately reset this behavior, select Allow the browser to use HTTP with the FlowForce hostname and reload the page so that the browser receives the updated header. |
You can select files using the Browse on Server button. The dialog provides guidance on which files to choose alongside the file picker.
This section enables you to select a cluster mode for this FlowForce instance. A cluster represents a group of several instances of FlowForce Server, running on different machines, that communicate for the purpose of executing jobs in parallel. A cluster consists of one master FlowForce Server and one or several workers. You can select any of the following options:
•Standalone: FlowForce Server runs as a single instance without a cluster.
•Worker: In this mode, the instance can execute only jobs assigned by the master. On the first login, a user with the Manage Cluster privilege will be forwarded to the Cluster Management page, where they will be able to send a request to join the master (see Operation in Worker Mode).
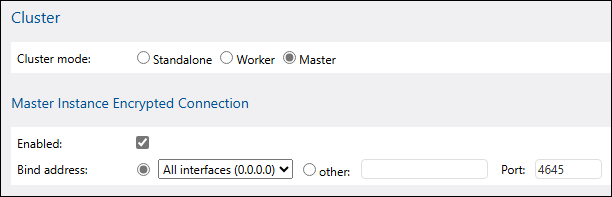
•Master: In master mode, FlowForce Server continuously evaluates job-triggering conditions and provides the FlowForce service interface. The master is aware of worker machines in the same cluster and may be configured to assign job instances to them, in addition to or instead of processing job instances itself.
To set the instance in master mode (screenshot below):
1.Check the Enabled check box.
2.Set the bind address and port. The port will be used for communication between the master and workers and must be different from the ports used by the FlowForce Server and FlowForce Web Server services. See also Operation in Master Mode.
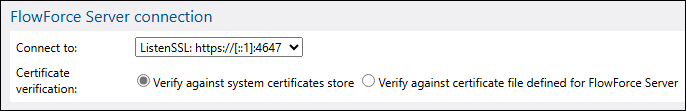
FlowForce Server connection (FlowForce Web only)
This setting allows selecting which binding to use for communication between FlowForce Web Server and Flow Force Server. Port binding must be enabled and must not be restricted to services only.
For HTTPS connections, this setting allows choosing how to verify the FlowForce certificate (screenshot below):
•Against the system certificates store (standard behavior): The certificate or CA that signed the certificate must be present in the system certificate store.
•Against Flow Force Server's certificate file: FlowForce Server checks that the certificate used during the connection matches the one specified in the Certificate File field of the HTTPS Certificate section.
You can set the default time zone for triggers. When you add a new trigger, the time zone will be pre-filled in the trigger's parameters. You can also set the default time zone via the Administration page.
Next step
After you have finished defining the network settings and other parameters, click Save Changes or Save and Apply to Running Services. This action will redirect you to the main Setup page. The next step is to install the services.