Job Distribution on FlowForce Server
FlowForce Server is Altova’s high-performance engine for automating workflows of XML processing, data integration, report generation, and more. It integrates with other Altova server software products to automate their functions, such as executing complex data integration processes, including ETL projects, designed in MapForce; running StyleVision report generation jobs; or validating XML, XBRL, or JSON files with RaptorXML Server.
Starting with Version 2019, FlowForce Server offers new options for distributed execution and load balancing to improve availability and performance. Let’s take a look at how configuring multiple FlowForce Servers to run as a cluster can help improve data throughput and provide redundancy.

Configuring multiple servers for high-availability with one “master” and multiple “worker” servers has benefits beyond ensuring uninterrupted performance. These include:
- Load balancing. When your business needs expand and you need additional scalability, it is possible to distribute the workload across multiple instances of FlowForce Server. You can set up a cluster comprised of a master machine and multiple worker machines and thus take advantage of all the licensed cores in the cluster.
- Improved resource management. The server instance designated as the master continuously monitors job triggers and allocates queued items to workers, or even to itself, depending on the configuration. You can control the queue settings and assign jobs to the appropriate queue as required. For example, you can optionally configure the master machine not to process any job instances at all to free up its resources and dedicate them exclusively to the continuous provisioning of FlowForce services.
- Smoother scheduled maintenance. Because multiple machines are handling jobs, IT can temporarily shut down any of the worker machines without impacting job processing.
Configuring FlowForce Server for Load Sharing
Each cluster of FlowForce Servers operates with one master server and any number of worker servers.
Please note that to enable load sharing, the corresponding Altova server software (e.g., MapForce Server, RaptorXML Server, etc.) must be installed on the master and all worker servers in the system.
When you first install FlowForce Server software, the FlowForce Server instance acts as the master of a one-machine cluster (which includes itself). To set up a cluster to distribute processing workload, install one or more additional FlowForce Server instances and convert them to “worker” mode.
If you’re running the software on a Windows server, you can designate the instance to be standalone, master, or worker during the installation process. Otherwise, you can access the cluster management interface in the Administration section of the web administration interface.
In either scenario, designating a server instance as a worker requires some configuration on the cluster management interface after installation as described here.
Job Distribution
Once your master and worker servers are designated, you can use the FlowForce Server on the master machine to set up job execution queues to control how job instances run. Each queue controls how many job instances in can be run at any time, the delay between runs, and so on.
You can configure a queue to run only on the master, only on workers, or on both depending on available server cores. It is also possible to define basic fallback criteria. For instance, a queue may be configured to run by default on master and all its workers; however, if all workers become unavailable, the queue will fall back to master server.
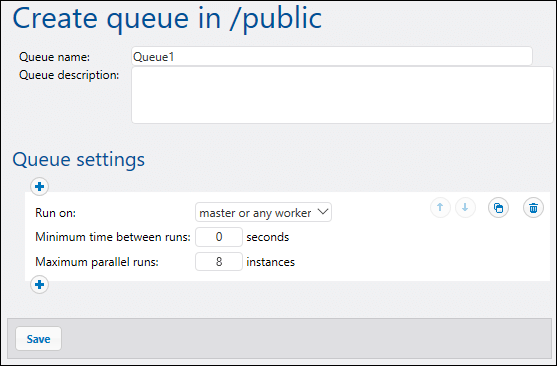
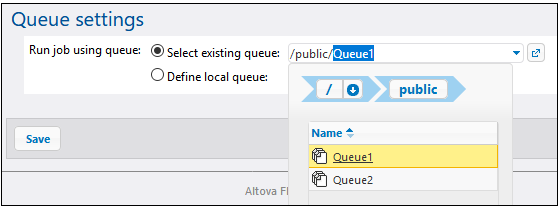
Once queue(s) are defined, you can configure each job to add it to the appropriate one.
Support for running multiple server instances as a cluster is available on FlowForce Server Advanced Edition.
