New XBRL Video
We recently posted a new, five-minute XBRL Overview video on YouTube! Please check it out and let us know what you think!
We recently posted a new, five-minute XBRL Overview video on YouTube! Please check it out and let us know what you think!
We have recently updated Altova’s MissionKit XBRL online training course, which debuted in May, to make the XBRL filing process as accessible to accountants and financial professionals as it is to more technical users. The new course includes easily identifiable “Accountant’s Notes” to make key XBRL concepts more transferable for those with an accounting background. An updated glossary also includes more accounting-friendly definitions of XBRL concepts to help you ease into the XBRL filing process. Access Altova’s MissionKit XBRL course now. (Yes, it’s free!)
Having recently returned from a short visit to the 19th XBRL International Conference in Paris, I can’t help but think that many organizations are simply missing the point – and that perhaps the SEC mandate is partly to blame for this. One would think (well, I thought, anyway) that in the year following the issuance of XBRL reporting requirements by the world’s largest economy, that this conference would be overflowing with company representatives eager to learn more about how, and best of all, why they should mark up their financial data in XBRL. But alas, this was not the case. I can only guess that the meager attendee numbers – especially from the United States – have to do with the fact that organizations are still viewing XBRL as singularly a compliance issue and are continuing to outsource the “tagging” of their financial statements to financial printers or other EDGAR filing entities. So, is XBRL a compliance issue? Well, of course it is, but it is much more than that. I can tell you this for certain because I work for Altova and we simply do not focus on compliance software. We build tools that help businesses to maximize the efficiency of their internal processes with an eye toward reducing the overall time and cost of the data management workflow. And this is well within the realm of possibility for any company using XBRL – but it means taking a proactive look at the way you manage your data. “Tagging” implies that financial statements are drawn up in the traditional manner in a spreadsheet or accounting program and then retroactively and meticulously marked up with XBRL tags to make them compliant. Ugh… no wonder compliance has such an ugly ring to it! Haven’t we all got enough work to do? And wait, isn’t this just adding one manual task on top of another – doubling the chances of human error? I’m not sure exactly when this word “tagging” became so popular for describing XBRL implementation, but all it has done is succeeded in oversimplifying something that was not very complicated in the first place (admittedly, it was probably coined by someone in the marketing tribe – of which I’m a member). Anyway, let’s put this idea of tagging aside and see if we can come up with something a little more dangerous. Let’s say that all of your company financial data resides in some sort of backend repository, a database, accounting/ERP system, XML, or even some combination of these. What if you could simply map your data to XBRL in-house instead of having external consultants comb through reports and tag each line item? What if you could even reuse this mapping the next time you had to produce a similar financial report? And what if you could even have your IT department automate your XBRL filing processes?
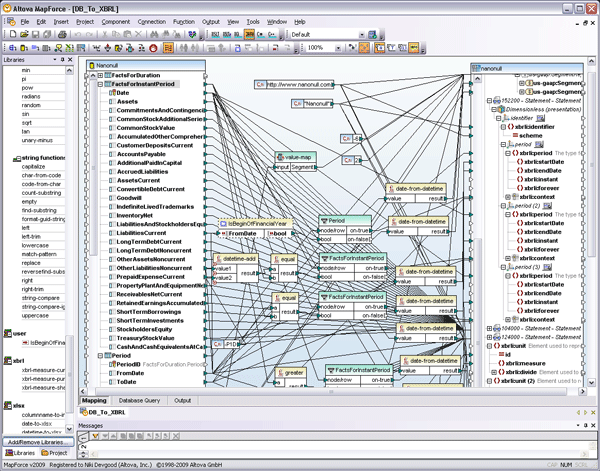
XBRL Mapping Altova MapForce is an enterprise-level data integration tool that lets you do just this. It is used at a high level by developers and application architects, but its easy-to-use graphical interface makes MapForce accessible to anyone with an understanding of the data that needs to be mapped. Let’s look at a partial example to illustrate how easy this can be: The first step is to load insert the source data component – in this case a database – into the MapForce design pane.
Note that the mapping component is a representation of the tables and columns in the database, the underlying data can, therefore, change at any time and the mapping itself will not be affected. The same is true for any mapping structure that you use in MapForce – XML, databases, flat files, EDI, Excel, XBRL, or Web services. Next, we’ll add our target mapping component, in this case a basic XBRL extension taxonomy built on top of US GAAP – Commercial and Industrial.
Now, we can simply begin the mapping by connecting lines to associate line items. There will be some cases when we need to apply data processing rules to slightly modify the format, filter data, or even add constants for XBRL reporting requirements that do not exist in the database. All of this is very easily done by dragging and dropping intermediary functions from the MapForce library in the sidebar. Let’s say, for example, that your database automatically requires a datetime format to record any accounting period. Since XBRL reporting only requires a date, we need to strip the time out in our mapping. So, simply drag a date-from-datetime function from the library and connect the lines between your database and XBRL component.
Of course, you’ll probably also need to add a variety of other math, logical, or other types of functions to your data, and you will find a long list of these already available in the function library.
You can also easily add custom functions, if needed, using a graphical function builder. In the end, your mapping will look something like this:
Now just hit the Output tab to see what the XBRL looks like. And there you go… a reusable, extensible data mapping that you can run any time you need to submit XBRL data. You can even integrate the mapping interface into another application, or ask IT to generate code that will automate the XBRL file generation each time a report is due. For a more detailed overview of how XBRL mapping works in MapForce, check our Altova’s XBRL tutorial.
So, here we have a very quick example of generating XBRL directly from an accounting system – no need for re-keying information, no need to create a set of traditional financial statements, and certainly no need for “tagging”. And best of all, all of this can easily be done in-house and at a fraction of the cost. Now don’t get me wrong, outsourcing could very well have a place in your company’s XBRL implementation. Building an XBRL extension taxonomy, for example, could very well be something that you feel more comfortable leaving to those who have years of experience working with XBRL syntax and other complexities. But putting your organization’s financial data into XBRL… shouldn’t that be left to those who know the data best? For more information on the Altova MissionKit tools for XBRL – which includes support for XBRL mapping and automation, XBRL validation and taxonomy creation, and XBRL rendering – please visit https://www.altova.com/solutions/xbrl-tools.html …or download the Altova MissionKit today!
We’re very excited to have just launched the next free Altova Online Training course: MissionKit XBRL! This comprehensive, five-module course provides an overview of XBRL and the Altova MissionKit for beginning and advanced technical users. After an introduction to XBRL and the XBRL filing process, you will learn to create an extension taxonomy in the XMLSpy XML editor. 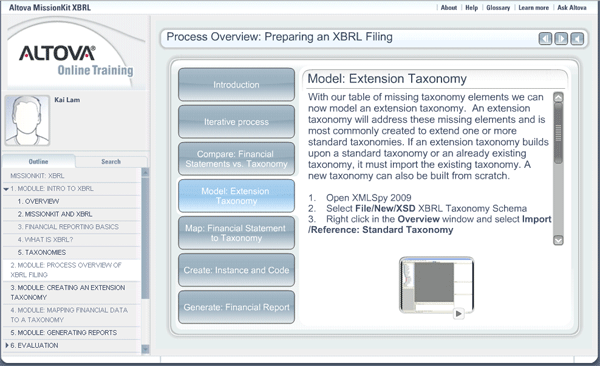 Then you’ll learn how to get your company’s back-end data into compliant XBRL filing documents using MapForce’s graphical data mapping interface, and explore how to automate this process by generating code in Java, C#, or C++. The final module completes the process and focuses on StyleVision and XBRL report generation. You’ll see how easy it is to create a straightforward XBRL report with drag-and-drop functionality to render XBRL in human-readable formats: HTML, PDF, and MS Word. The XBRL training course includes over 30 instructional videos, and the training is now delivered through Amazon’s S3 cloud services to ensure fast downloads and smooth video. You can even test what you’ve learned using the interactive quizzes for each module. Like all Altova Online Training courses, MissionKit XBRL is available on-demand, so that you can complete the courses as your schedule allows. And did I mention that it’s free? This course is currently in beta, and we’d appreciate your feedback to improve it. Please feel free to comment here or by completing the Altova Training Survey at the end of the course.
Then you’ll learn how to get your company’s back-end data into compliant XBRL filing documents using MapForce’s graphical data mapping interface, and explore how to automate this process by generating code in Java, C#, or C++. The final module completes the process and focuses on StyleVision and XBRL report generation. You’ll see how easy it is to create a straightforward XBRL report with drag-and-drop functionality to render XBRL in human-readable formats: HTML, PDF, and MS Word. The XBRL training course includes over 30 instructional videos, and the training is now delivered through Amazon’s S3 cloud services to ensure fast downloads and smooth video. You can even test what you’ve learned using the interactive quizzes for each module. Like all Altova Online Training courses, MissionKit XBRL is available on-demand, so that you can complete the courses as your schedule allows. And did I mention that it’s free? This course is currently in beta, and we’d appreciate your feedback to improve it. Please feel free to comment here or by completing the Altova Training Survey at the end of the course.
Last week, while giving a demo of the new XBRL capabilities in the Altova MissionKit, we stumbled across an interesting question: What is the best way for a semi-technical SME (in this case a CPA) to navigate a large XML/XBRL document for data entry? XMLSpy, which is included in the MissionKit tool suite, has a lot of cool features and different views for XML data, including the ever-popular grid view for visualizing the hierarchical structure of an instance document in a graphical manner. The ability to easily expand and collapse containers and drag and drop to change position makes XMLSpy’s grid view a pretty good choice for the task. 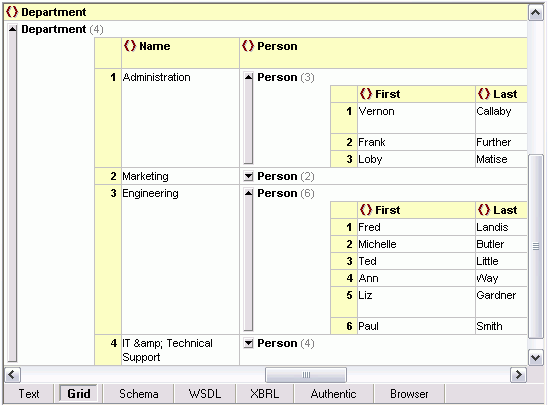 Of course let’s not forget that the XMLSpy XML editor also has a Find feature that would enable users to simply press Ctrl F or use the Find in Files window to find any element that they are looking for… but alas, in the case of XBRL, where element names are mindbogglingly verbose, this may be a challenge. Consider, for example, the US-GAAP’s aptly named <us-gaap:IncomeLossFromContinuingOperationsBeforeIncomeTaxesMinorityInterestAnd IncomeLossFromEquityMethodInvestments>. Not so much fun to type into a Find dialog… Our solution, therefore, and the winner for the easiest and most comprehensive way for even a non-technical user to find XML elements in a large document, utilizes a combination of longstanding XMLSpy features (the XPath Analyzer window) and a new feature in XMLSpy v2009, XPath auto-completion. Simply begin typing the element name in the XPath Analyzer window, and XMLSpy will show you all of the possibilities. Next, choose the one you are looking for, and XMLSpy will navigate directly to that node in the XML document.
Of course let’s not forget that the XMLSpy XML editor also has a Find feature that would enable users to simply press Ctrl F or use the Find in Files window to find any element that they are looking for… but alas, in the case of XBRL, where element names are mindbogglingly verbose, this may be a challenge. Consider, for example, the US-GAAP’s aptly named <us-gaap:IncomeLossFromContinuingOperationsBeforeIncomeTaxesMinorityInterestAnd IncomeLossFromEquityMethodInvestments>. Not so much fun to type into a Find dialog… Our solution, therefore, and the winner for the easiest and most comprehensive way for even a non-technical user to find XML elements in a large document, utilizes a combination of longstanding XMLSpy features (the XPath Analyzer window) and a new feature in XMLSpy v2009, XPath auto-completion. Simply begin typing the element name in the XPath Analyzer window, and XMLSpy will show you all of the possibilities. Next, choose the one you are looking for, and XMLSpy will navigate directly to that node in the XML document. 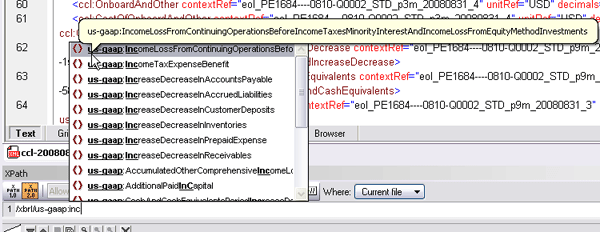 Now that was easy! And better yet, you get to tell your friends that you know XPath. 😉 Of course, for developers, intelligent XPath auto-completion provides a lot more than the ability to find a node quickly. As you type, it provides you with valid XPath functions, as well as element and attribute names from the associated schema and XML instance(s). XMLSpy accounts for namespaces when listing options and even provides deep path suggestions when the required node is not in close proximity to the current context. XMLSpy is available standalone or as part of the award-winning MissionKit tool suite.
Now that was easy! And better yet, you get to tell your friends that you know XPath. 😉 Of course, for developers, intelligent XPath auto-completion provides a lot more than the ability to find a node quickly. As you type, it provides you with valid XPath functions, as well as element and attribute names from the associated schema and XML instance(s). XMLSpy accounts for namespaces when listing options and even provides deep path suggestions when the required node is not in close proximity to the current context. XMLSpy is available standalone or as part of the award-winning MissionKit tool suite.
 Earlier this week we blogged about the release of Version 2009 of Altova MissionKit, which includes the complete Altova product line. One of the major themes in this latest release is comprehensive support for XBRL across multiple Altova MissionKit tools, so lets look into XBRL itself and the new functionality in more detail.
Earlier this week we blogged about the release of Version 2009 of Altova MissionKit, which includes the complete Altova product line. One of the major themes in this latest release is comprehensive support for XBRL across multiple Altova MissionKit tools, so lets look into XBRL itself and the new functionality in more detail.
The eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) is an XML-based vocabulary for electronic transmission of business and financial data. Currently in version 2.1, XBRL is an open standard that is maintained by XBRL International, a global non-profit consortium of over 550 major companies, organizations, and government agencies. XBRL was developed to facilitate business intelligence (BI) automation by enabling machine-to-machine communication and data processing for financial information with an eye towards cost reduction through the elimination of time consuming and error-prone human interaction. Official support from European Parliament and a mandate the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has all but secured XBRL’s future as the official standard for financial reporting. You can learn a lot more about the nuts and bolts of XBRL in the XBRL white paper written by Altova’s Technical Marketing Manager, Liz Andrews.
All of the power and functionality that XBRL brings to financial data is useless without XBRL-conformant tools to interpret and process this data. In fact, understanding the importance of tools for XBRL, the XBRL recommendation writes software vendors into its abstract:
XBRL allows software vendors, programmers, intermediaries in the preparation and distribution process and end users who adopt it as a specification to enhance the creation, exchange, and comparison of business reporting information.
As such, XBRL development and data integration can be supported in a variety of different ways. The Altova MissionKit 2009 provides comprehensive support for working with XBRL, from validation and editing, to transformation and rendering, in multiple tools: XMLSpy 2009 – XBRL validator and XBRL taxonomy editor. When you need to ensure that your XBRL filing documents are valid and compliant, XMLSpy can be used to to validate an XBRL instance file against its corresponding taxonomy. If you need to extend a standard taxonomy to meet your organization’s filing needs, the graphical XBRL taxonomy editor in XMLSpy gives you a graphical model with tabs that organize different types of taxonomy elements, wizards, and entry helpers, all of which guide data input based on the structural information provided in the XBRL instance and base taxonomies. 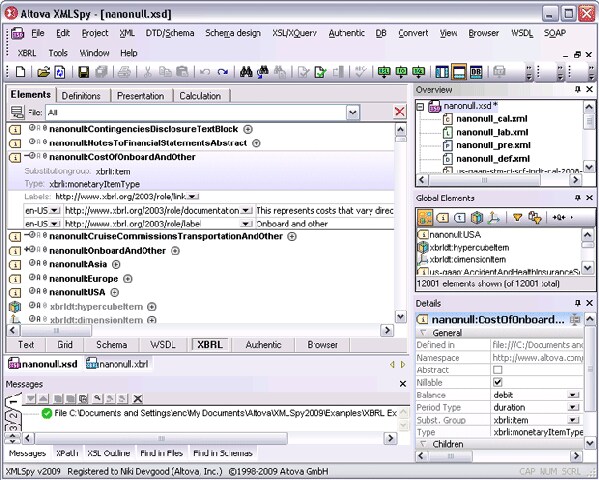 MapForce 2009 – XBRL exchange and data integration tool. When you need to extract financial data from back end systems and transform it into compliant XBRL filings, MapForce makes it easy with drag-and-drop, graphical data mapping and instant conversion. MapForce allows bi-directional data mapping between XBRL and databases, flat files, Excel 2007, XML, and Web services. Once your mapping project is defined, you can utilize it to automate quarterly and annual XBRL filing generation by transforming data with the MapForce UI, command line, or auto-generated, royalty free application code. This makes public financial data submission a repeatable and highly manageable process, allowing organizations to produce valid XBRL reports as required based on the variable data stored in accounting system fields – without having to define new mappings every quarter.
MapForce 2009 – XBRL exchange and data integration tool. When you need to extract financial data from back end systems and transform it into compliant XBRL filings, MapForce makes it easy with drag-and-drop, graphical data mapping and instant conversion. MapForce allows bi-directional data mapping between XBRL and databases, flat files, Excel 2007, XML, and Web services. Once your mapping project is defined, you can utilize it to automate quarterly and annual XBRL filing generation by transforming data with the MapForce UI, command line, or auto-generated, royalty free application code. This makes public financial data submission a repeatable and highly manageable process, allowing organizations to produce valid XBRL reports as required based on the variable data stored in accounting system fields – without having to define new mappings every quarter. 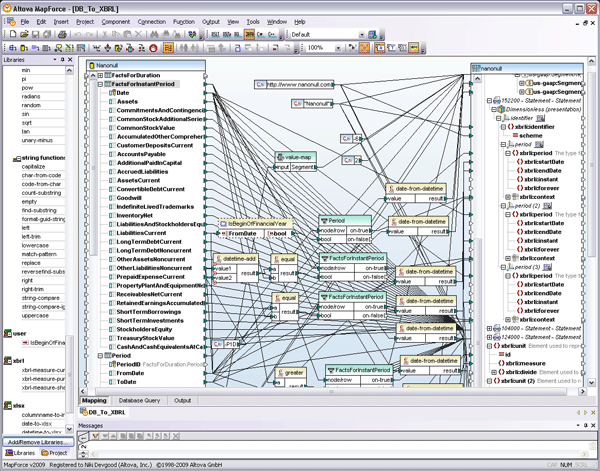 If you need to aggregate XBRL filings from different time periods or different organizations in your back end systems for analysis, MapForce lets you map the XBRL data to databases, flat files, XML – even Web services. Mapping data directly from its source format removes the need for re-keying and potential errors. Together, MapForce and XBRL enable the automation of the multi-dimensional financial analysis that organizations and stakeholders use to evaluate market, company, and industry performance on a regular basis. StyleVision 2009 – XBRL rendering tool. Once data is in XBRL format, and it’s time to render it for consumption on the Web or in printed materials, StyleVision lets you create a straightforward XBRL report to output the data in multiple formats. Simply drag and drop a taxonomy financial statement onto the design pane as an XBRL table, and then use StyleVision’s graphical interface to format stylesheets for simultaneous output in HTML, RTF, PDF, and Word 2007 (OOXML). The XBRL Table Wizard makes it easy to customize the table structure and specify the concepts to include in the report. In the case of the US-GAAP taxonomy, which provides, in addition to the hierarchical organization in its presentation linkbase, some best practices information on how to structure XBRL instances, you can simply select US-GAAP mode to have StyleVision automatically output the data according to this information.
If you need to aggregate XBRL filings from different time periods or different organizations in your back end systems for analysis, MapForce lets you map the XBRL data to databases, flat files, XML – even Web services. Mapping data directly from its source format removes the need for re-keying and potential errors. Together, MapForce and XBRL enable the automation of the multi-dimensional financial analysis that organizations and stakeholders use to evaluate market, company, and industry performance on a regular basis. StyleVision 2009 – XBRL rendering tool. Once data is in XBRL format, and it’s time to render it for consumption on the Web or in printed materials, StyleVision lets you create a straightforward XBRL report to output the data in multiple formats. Simply drag and drop a taxonomy financial statement onto the design pane as an XBRL table, and then use StyleVision’s graphical interface to format stylesheets for simultaneous output in HTML, RTF, PDF, and Word 2007 (OOXML). The XBRL Table Wizard makes it easy to customize the table structure and specify the concepts to include in the report. In the case of the US-GAAP taxonomy, which provides, in addition to the hierarchical organization in its presentation linkbase, some best practices information on how to structure XBRL instances, you can simply select US-GAAP mode to have StyleVision automatically output the data according to this information. 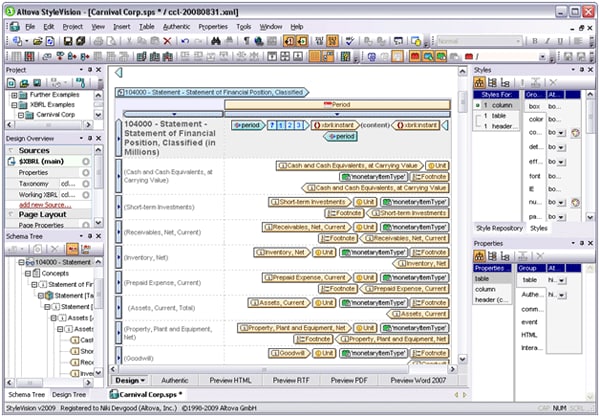 To try this powerful XBRL functionality for yourself, download a free, fully functional 30-day trial of the Altova MissionKit 2009, and please let us know what you think by commenting on this blog or in the Altova Discussion Forum.
To try this powerful XBRL functionality for yourself, download a free, fully functional 30-day trial of the Altova MissionKit 2009, and please let us know what you think by commenting on this blog or in the Altova Discussion Forum.
We are very excited to announce general availability of the Altova MissionKit 2009 suite of XML, database, and UML tools. Version 2009 delivers numerous new features across the tools included in the MissionKit, including comprehensive support for working with XBRL, native support for new databases and database differencing, UML sequence diagram generation, and much more. A few details are below, with complete information and screenshots available on the Altova What’s New page. Coinciding with this major release, we have decided to pass savings realized due to the currently favorable US$/EUR exchange rate directly to our customers by reducing US$ prices across the entire Version 2009 product line.
The Altova MissionKit 2009 provides powerful new support for viewing, editing, validating, mapping, and publishing XBRL data. With intelligent wizards, graphical drag-and-drop design models, and various code generation capabilities, the MissionKit Version 2009 gives developers, technical professionals, and power users one easy-to-use suite of tools for working with XBRL and transforming data into content that can be shared with business partners, stakeholders, and regulatory commissions. Altova MissionKit tools with XBRL support are:

Native support for additional databases has been added to all database-enabled Altova MissionKit tools, including XMLSpy 2009, MapForce 2009, DatabaseSpy 2009, StyleVision 2009, and DiffDog 2009. Current support for SQL Server® and Oracle® databases is now extended to include the most recent versions – SQL Server 2008 and Oracle 11g. New support for the PostgreSQL 8 database is also now available. In addition, both DatabaseSpy 2009 and DiffDog 2009 now allow you to compare and merge database content. Individual database tables or multiple tables within a schema can be compared, whether they are the same database type or completely different databases. Results of the content comparisons are displayed in tables, and differences can be merged bi-directionally. This new database comparison functionality allows users to easily backup, copy, or merge data quickly and easily. 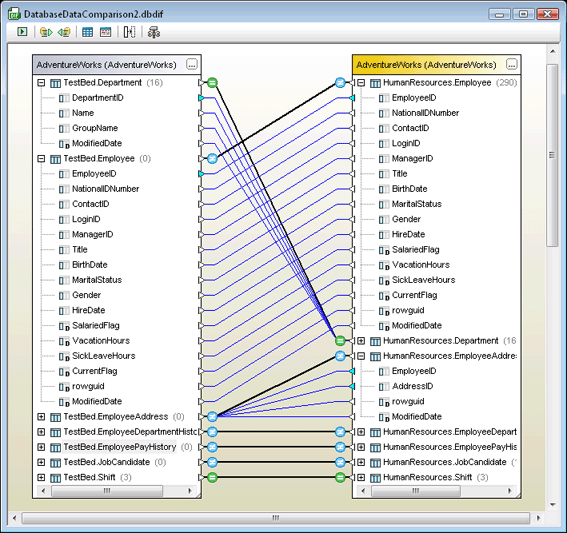
MissionKit users working with UML will be especially interested in this new functionality in UModel 2009. Sequence diagram generation greatly assists developers who need to reverse engineer existing applications written in Java, C#, or Visual Basic. After importing an existing project, directory, or file into a UModel 2009 project, you can now select any operation in any class, and automatically generate a sequence diagram that illustrates the lifecycle of the operation, as well as objects that interact with it. Like all other project diagrams in UModel, sequence diagrams are stored as part of the UModel project file and can be included in generated UModel project documentation. Check out the full list of features added in Version 2009, and be sure to check back here frequently, as we’ll be blogging about more new features each week. As always, you can download a free trial of the Altova MissionKit to test out this new functionality for yourself.
