Software engineers have long wanted to create an application once and run it on multiple platforms. With today’s rapidly evolving mobile devices, the problem is even more urgent, as iOS, Android, Windows Phone, and Surface tablets all compete for developer resources.
If you’re working on apps to communicate with enterprise users, you risk disenfranchising and alienating influential and important subsets of your colleagues when you build for each device sequentially or deliver unequal functionality.
Altova MobileTogether lets you create a cross-platform mobile solution once and deploy it in seconds to all mobile users in the enterprise, who may run it on iPhones, iPads, Android phones or tablets, Windows Phones, Surface tablets, or even laptop or desktop computers.
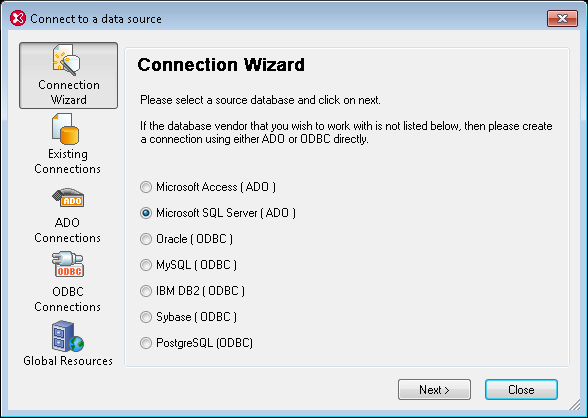
And these are not simple .html-based one-size-fits-all Web pages, but true native mobile solutions that take advantage of all the rich interface features users already know, delivering mission-critical data from databases, XML files, or by issuing HTTP requests to remote servers and filtering and formatting the response as necessary.

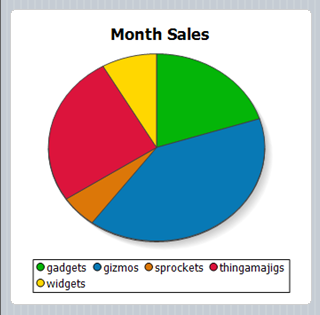
The MobileTogether Designer is an easy-to-use development tool for creating high-quality business intelligence dashboards, interactive reports, enterprise forms, and other mobile applications by using drag-and-drop functionality. You simply drag various controls into the work area and assign data structures and actions to build a cross-platform solution.
Read more…



























 Or, to go in the other direction, it’s just as easy to
Or, to go in the other direction, it’s just as easy to 