HL7 Data Integration
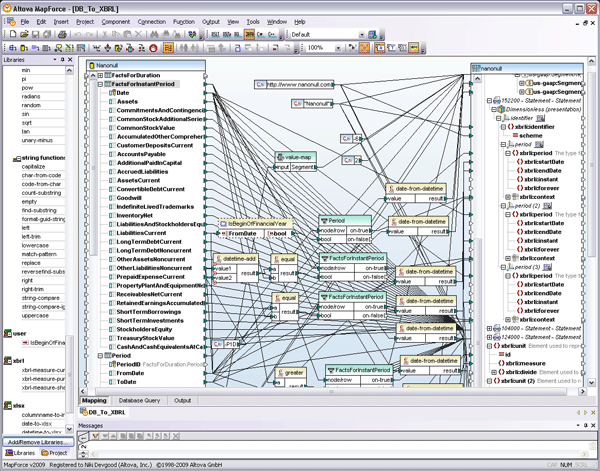
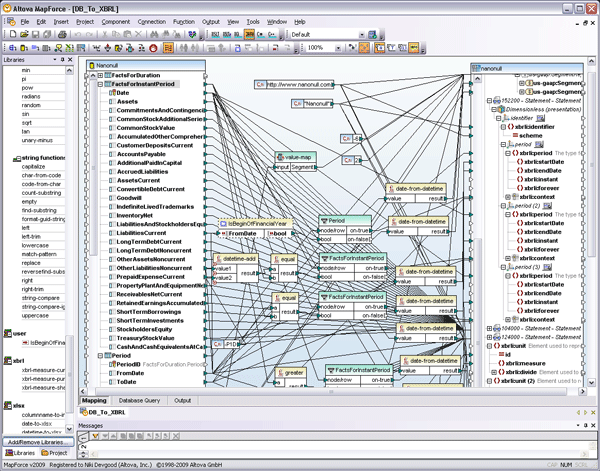
By now, you may be aware of the global push that is being made for data transparency – both in the realm of financial reporting* with a recent XBRL mandate in the U.S., and electronic health records – and that these efforts are focused on the creation and maintenance of XML standards. Of course most of you are among the XML savvy and can feel free to please join me in a resounding “duh” to the rest of the world that is only now beginning to realize the value of XML data in reducing errors, lowering costs, and generally increasing the overall efficiency of data management. But for now, let’s focus a bit on healthcare data and standards. Both HL7 and the HIPAA mandated X12N formats healthcare data exchange have traditionally been EDI-based, but the newest version of HL7 (version 3.x), released in 2005 is XML-based and constrained by a formal framework (HDF) that allows for an evolving data model within a carefully defined development methodology. Yes people, standards – bring it on!! Well, of course there is a need to map this data from the HL7 EDI to HL7 XML, to and from backend systems, to Web services and beyond. So what now? Do you need to become an expert in all of these formats? Weren’t standards supposed to make things EASIER? Please ladies and gentleman, return to your seats! Let me draw your attention once again to MapForce, the coolest data integration tool on the market, with support for mapping and converting data to and from XML, databases, flat files, EDI (including HL7, X12, and EDIFACT), Excel 2007, and Web services. 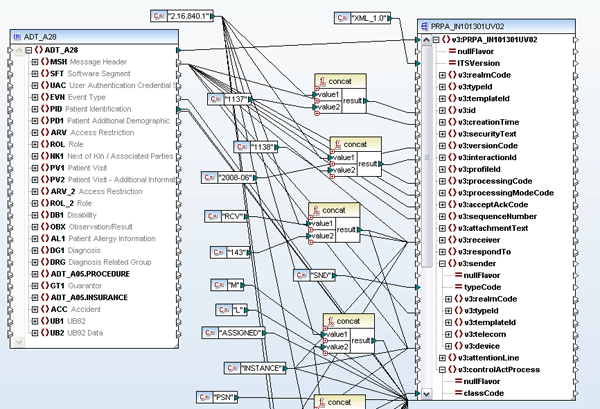 The shot above shows a simple graphical mapping updating an HL7 v2.6 message to v3.x. Altova MapForce is an any-to-any visual data mapping tool that supports mapping HL7 data, in its legacy EDI or newer XML-based format, to and from XML, databases, flat files, other EDI formats, and Web services. Mappings are implemented by simply importing the necessary data structures (MapForce ships with configuration files for the latest EDI standards and offers the full set of past and present HL7 standards as a free download) and dragging lines to connect nodes. A built-in function library lets you add advanced data filters and functions to further manipulate the output data. MapForce can also facilitate the automation of your HL7 transaction workflow through code generation in Java, C#, or C++ and an accessible command line interface. Additional support for mapping HL7 data to and from Web services gives healthcare organizations the ability to meet new technology challenges and changing enterprise infrastructures as they unfold within internal and external provider domains. Read more on our new HL7 tools page in the Altova Solutions Center. *The Altova MissionKit has been infused with XBRL support to meet financial reporting mandates.
The shot above shows a simple graphical mapping updating an HL7 v2.6 message to v3.x. Altova MapForce is an any-to-any visual data mapping tool that supports mapping HL7 data, in its legacy EDI or newer XML-based format, to and from XML, databases, flat files, other EDI formats, and Web services. Mappings are implemented by simply importing the necessary data structures (MapForce ships with configuration files for the latest EDI standards and offers the full set of past and present HL7 standards as a free download) and dragging lines to connect nodes. A built-in function library lets you add advanced data filters and functions to further manipulate the output data. MapForce can also facilitate the automation of your HL7 transaction workflow through code generation in Java, C#, or C++ and an accessible command line interface. Additional support for mapping HL7 data to and from Web services gives healthcare organizations the ability to meet new technology challenges and changing enterprise infrastructures as they unfold within internal and external provider domains. Read more on our new HL7 tools page in the Altova Solutions Center. *The Altova MissionKit has been infused with XBRL support to meet financial reporting mandates.




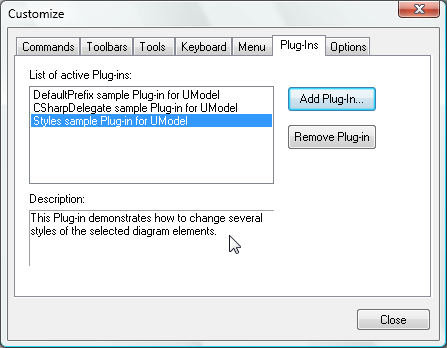 The screen shot below shows UModel with several custom plug-ins installed. PlugInMenu3 adds the prefix m_ to the name whenever a new property is created in a class.
The screen shot below shows UModel with several custom plug-ins installed. PlugInMenu3 adds the prefix m_ to the name whenever a new property is created in a class. 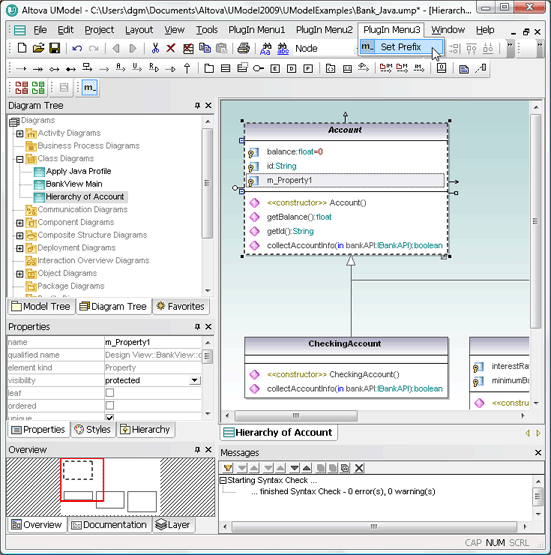 Note the plug-in custom toolbars directly above the Diagram Tree. The custom toolbar at the far left lets the user choose red or green to fill all currently-selected diagram elements. The Set Prefix toolbar lets the user turn the prefix feature on or off. If you want to try out the sample plug-ins yourself you can compile the sample code and add the resulting .dll files in the UModel Customize dialog. If you want to deploy the plug-ins across multiple workstations by sharing the .dll files, you will also have to register them manually at each workstation.
Note the plug-in custom toolbars directly above the Diagram Tree. The custom toolbar at the far left lets the user choose red or green to fill all currently-selected diagram elements. The Set Prefix toolbar lets the user turn the prefix feature on or off. If you want to try out the sample plug-ins yourself you can compile the sample code and add the resulting .dll files in the UModel Customize dialog. If you want to deploy the plug-ins across multiple workstations by sharing the .dll files, you will also have to register them manually at each workstation.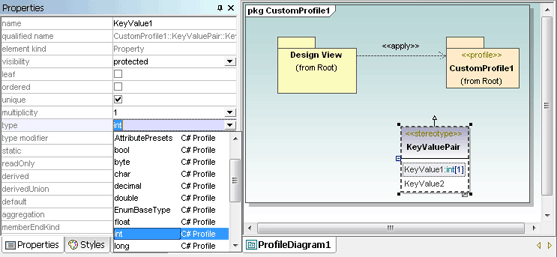 We are interested to hear about the applications users devise for the UModel API, plug-ins, and custom stereotypes over the coming weeks. You can add a comment to this blog entry, exchange tips with other users in the
We are interested to hear about the applications users devise for the UModel API, plug-ins, and custom stereotypes over the coming weeks. You can add a comment to this blog entry, exchange tips with other users in the 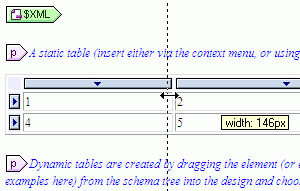

 MapForce 2009 –
MapForce 2009 –